What Is Healthcare Analytics and Why Is It Important?

Let’s face it: data is everywhere, especially in healthcare. From electronic health records to patient-reported outcomes, data piles up and can feel overwhelming without the tools and resources to make sense of it.
Applying big data analytics is the solution. Read on for an introduction to healthcare data analytics, including the types, uses, value, and potential future of data analytics in healthcare.
In this post we will cover:
- What Is Data Analytics in Healthcare?
- What Is the Role of Data Analytics in Healthcare?
- What Are the Types of Healthcare Analytics?
- How Is Healthcare Analytics Used?
- What Is the Value of Healthcare Analytics?
- What Is the Future of Data Analytics in Healthcare?
What Is Data Analytics in Healthcare?
In general, big data analytics is the practice of using analytical techniques to make sense of large sets of diverse data. [1] In healthcare, unwieldy data sets are the norm. A comprehensive data entry for a single patient could include everything from electronic health record data and physician notes to imaging, prescriptions, lab results, insurance, monitoring equipment output, and even social media posts.
Data sets like these are often impossible to analyze on more general, commonly used software platforms and hardware systems. [1] This is where the application of big data analytics in healthcare becomes a must-have instead of just a nice-to-have.
Advancing healthcare and improving patients’ lives requires both measurement and extensive analysis of these large sets of healthcare data to glean valuable, actionable insights. [1] Physicians, researchers, medical specialty societies, pharmaceutical companies, and every other healthcare stakeholder can then use these insights as jumping-off points for improvement.
What Is the Role of Data Analytics in Healthcare?
The role of data analytics in healthcare is clear: Pull the signal from the noise.
Whether you need to improve quality, advance research, manage risk, or anything in between, you have access to mountains of data. However, just having the data won’t do you much good if you don’t have a systematized way to organize, analyze, and interpret it.
This is one of the reasons why data analytics is so important in healthcare. By using analytical techniques, you can not only make sense of the past, but also chart a course for the future, for the benefit of the entire healthcare community.
What Are the Types of Healthcare Analytics?
One of the benefits of data analytics in healthcare is that there are many types you can use to answer many questions.
Let’s say you’re interested in readmission rates after surgical procedures. You’ll want to answer questions like: How did hospital readmission rates change over the past five years? What surgical procedures were associated with the highest readmission rates? What will readmission rates look like over the next year without any interventions? How could a potential intervention affect readmissions?
Healthcare analytics can help answer all of these questions. Let’s dive deeper into the four main types of healthcare analytics, their definitions, what questions they answer, and the potential limitations of each.
- Descriptive analytics uses data from the past to provide insights around trends or benchmarks, usually in the form of a dashboard. While descriptive analytics helps us understand what happened in the past, it is unable to provide strong insights to influence future health outcomes or provide foresight into potential future events.
- Predictive analytics uses modeling and forecasting to determine what is likely to happen next. Predicting the future is useful, but results are predicated on all conditions remaining the same. Predictive analytics is unable to provide insight into what might happen after an intervention or other change.
- Prescriptive analytics uses machine learning to suggest a course of action or strategy by taking in numerous inputs. Prescriptive analytics helps us understand what the effects of a specific action will be, but the inherent uncertainty and limited maturity of this type of analytics could lead to implementing suboptimal actions.
- Discovery analytics uses machine learning to analyze raw data to determine interconnections, patterns, and outliers. Discovery analytics helps us understand what we need to explore further, but raw data can be incomplete or inaccurate, limiting its usefulness.
How Is Healthcare Analytics Used?
Data analytics can help improve healthcare for all industry stakeholders, from health systems and physicians to patients, pharmaceutical and medical device companies, and specialty societies.
The many uses of big data analytics in healthcare can be organized into four main buckets. Healthcare analytics can help your organization enhance its competitive position, improve quality, advance research initiatives, and manage risk and reporting.

To tap into these key uses of healthcare analytics, you need cutting-edge software and a trusted process to take you from an unmanageable jumble of data to actionable, real-world evidence.
That process involves:
- Acquiring the data: Whether you use machine-to-machine data transfer, patient surveys, employed nurses abstracting data from case files, or all of the above, all data needs to be collected in one place.
- Transforming the data: Here, the data is cleaned, validated, and analyzed to answer research questions.
- Acting on the analytical insights: Leverage real-world evidence to reach your organization’s goals.
In addition, you’ll want to make sure your data analytics software solution is flexible enough to evolve with your needs, and that it’s built with high-level security features in place. That way, you’ll have everything you need to unlock the greatest possible value from your data.
What Is the Value of Healthcare Analytics?
Beyond its many uses, healthcare analytics provides real-world value to those who act on analytical insights. Below, you’ll find an example of a health industry player that has reaped the benefits of using big data analytics in healthcare.
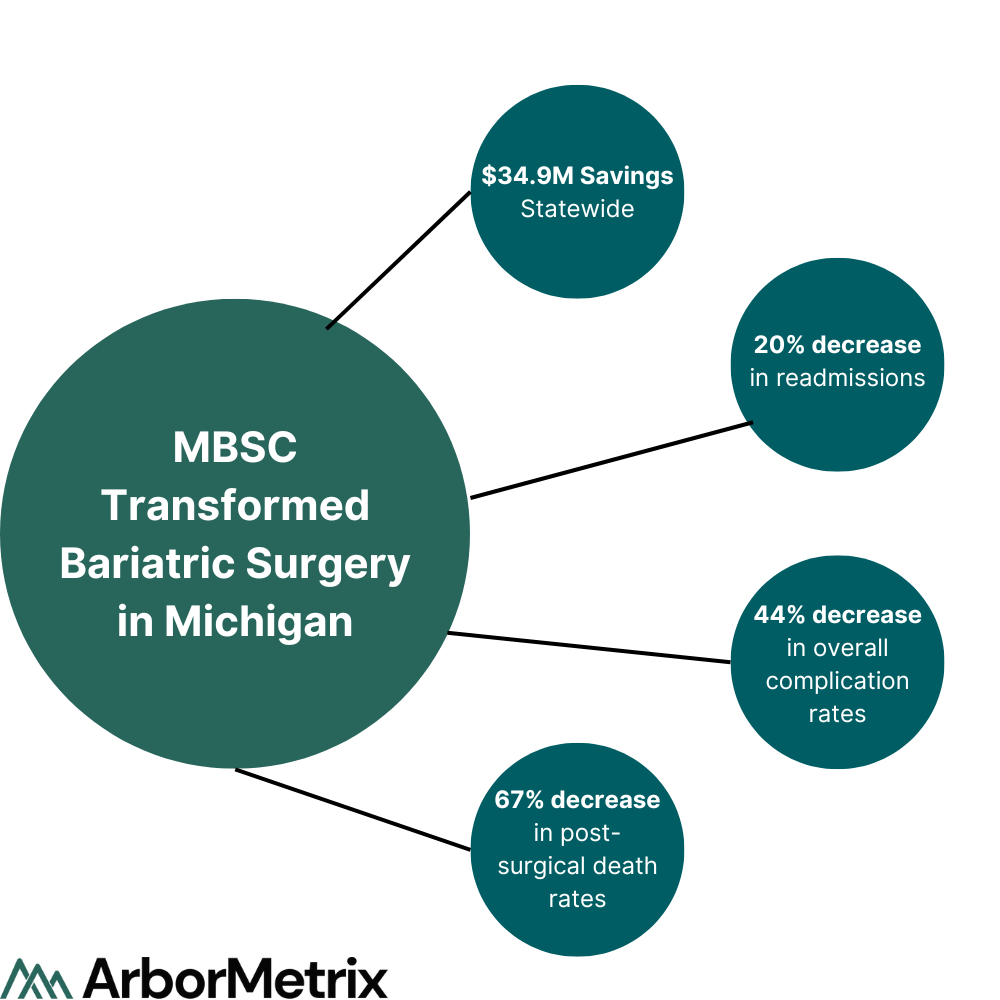
The Michigan Bariatric Surgery Collaborative (MBSC) Reduced Post-Surgical Death Rates by 67%
MBSC, a quality improvement collaborative funded by Blue Cross Blue Shield, leverages a powerful patient registry to improve bariatric surgery in Michigan. MBSC used the ArborMetrix platform to power outcomes calculators, patient-reported outcomes, and video surgical analysis, resulting in a 67% decrease in post-surgical death rates and $35 million in statewide savings, among other impressive results.
What Is the Future of Data Analytics in Healthcare?
New technologies are continuing to emerge that push the boundaries of how healthcare analytics can be used. From artificial intelligence to machine learning to natural language processing, the true future of healthcare is in wielding these technologies for greater impact.
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to a collection of technologies that can autonomously think and adapt with intention. [3,4] In healthcare, AI can use input data to diagnose disease, structure clinical trial cohorts, and identify malignant tumors, among many other uses.
Machine learning and natural language processing are subsets of AI. Machine learning involves generating models to describe data. As more data is introduced, the algorithms adapt to the new information to create models that fit the data as accurately as possible. [3] Machine learning is often used in precision medicine in a predictive capacity—given a patient’s unique medical history, machine learning techniques can predict what treatment is most appropriate.
Natural language processing (NLP) uses various techniques to make sense of human-generated speech or writing. [3] NLP is especially useful for extracting information from patient records and classifying clinical documents.
This is just a taste of what’s in store for healthcare data analytics. With technology advancing at a rapid clip, new discoveries that can create even greater impact are inevitable.
-